Modern Data Management Platforms vs
Traditional Data Warehouses:
Understanding the Key Differences
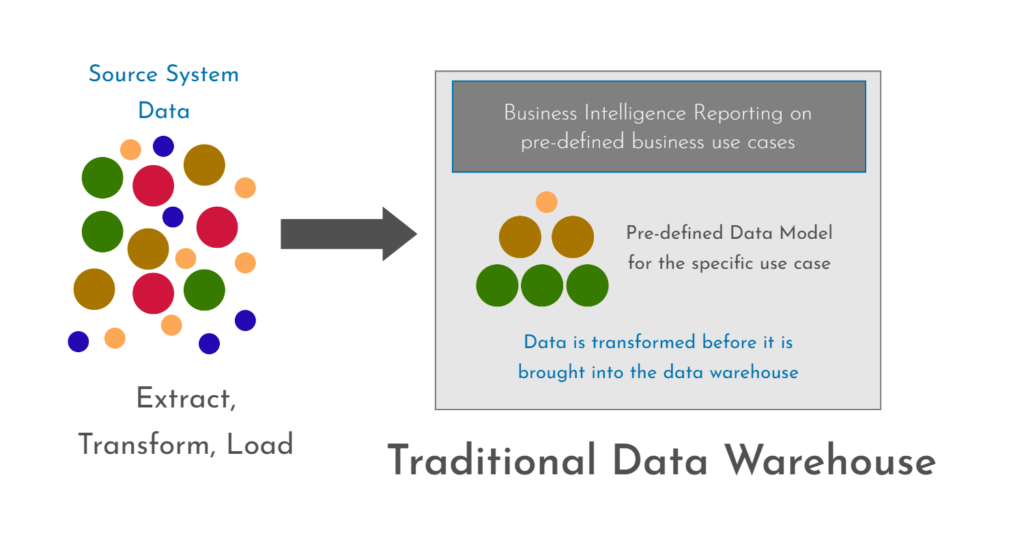
A modern data management platform and a traditional data warehouse have distinct differences in terms of their capabilities and purposes. Here are some of the main differences:
- Data Ingestion: A modern data management platform can ingest both structured and unstructured data from various sources, including social media, IoT devices, and other digital platforms. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to work with a wider range of data types. A traditional data warehouse, on the other hand, typically requires upfront modeling and is designed to handle structured data from specific sources.
- Upfront Modeling: A traditional data warehouse requires upfront modeling and structuring of data before it can be loaded into the system. This can be time-consuming and expensive, as it requires a team of data architects to design and implement the necessary data models. In contrast, a modern data management platform often uses a schema-on-read approach, which allows for more agile and flexible data exploration without the need for upfront modeling.
- Digital Transformation: A modern data management platform is designed to cater to an organization’s digital transformation requirements. This includes both transactional and analytical purposes, allowing organizations to build modern data-driven applications that can respond to real-time data insights. A traditional data warehouse, on the other hand, is primarily designed for analytical purposes, and is less suited to handling real-time data.
- Scalability: A modern data management platform is typically built on cloud-native architecture, which allows for greater scalability and elasticity than a traditional data warehouse. This means that organizations can quickly and easily scale their data management capabilities up or down as needed, depending on changing business requirements.
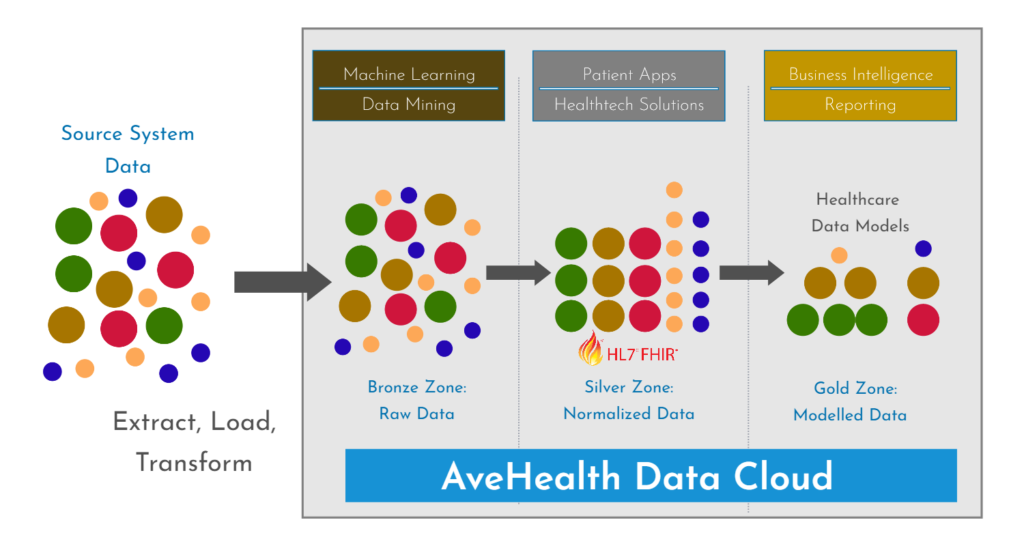
In summary, a modern data management platform like the AveHealth Data Cloud offers greater flexibility, agility, and scalability than a traditional data warehouse. It is better suited to handling diverse data types, supporting digital transformation initiatives, and enabling real-time data insights for both transactional and analytical purposes.
